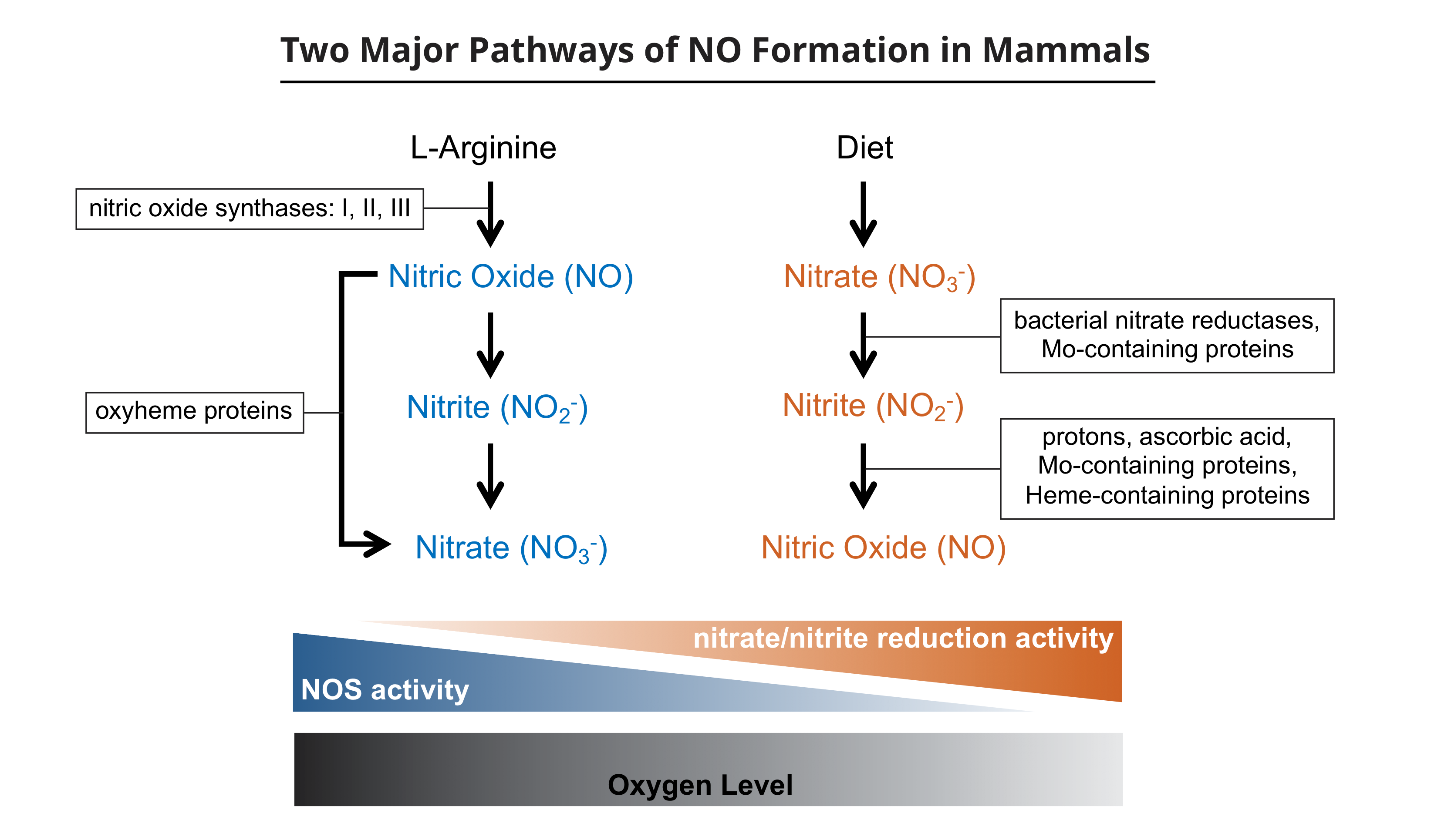
Nitric oxide (NO) cycle. NO2⁻: nitrite anion; NO3⁻: nitrate anion; NO

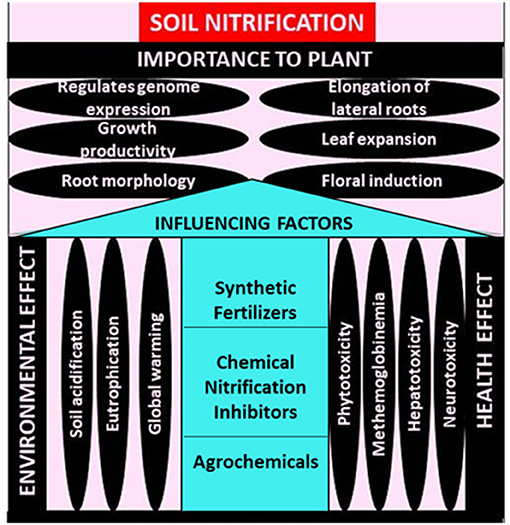
Frontiers Factors Influencing Soil Nitrification Process and the Effect on Environment and Health

Visualization of NO3⁻/NO2⁻ Dynamics in Living Cells by Fluorescence Resonance Energy Transfer (FRET) Imaging Employing a Rhizobial Two-component Regulatory System. - Abstract - Europe PMC
Why does an aqueous electrolytic cell nitrate ion never react at the anode but nitrite ions do? - Quora

Visualization of NO3⁻/NO2⁻ Dynamics in Living Cells by Fluorescence Resonance Energy Transfer (FRET) Imaging Employing a Rhizobial Two-component Regulatory System. - Abstract - Europe PMC

Nitrate reduction to NO 2 and nitric oxide as reported by Tsai et al. 49

The nitrate–nitrite–nitric oxide pathway in physiology and therapeutics

Decrease of nitrogen cycle gene abundance and promotion of soil microbial-N saturation restrain increases in N2O emissions in a temperate forest with long-term nitrogen addition - ScienceDirect

The nitrate–nitrite–nitric oxide pathway in physiology and therapeutics
Nitric Oxide Formation Research

Visualization of NO3⁻/NO2⁻ Dynamics in Living Cells by Fluorescence Resonance Energy Transfer (FRET) Imaging Employing a Rhizobial Two-component Regulatory System. - Abstract - Europe PMC

Recent Advances in Electrocatalytic Hydrogenation Reactions on Copper‐Based Catalysts - Zheng - Advanced Materials - Wiley Online Library

Nitric oxide (NO) cycle. NO2⁻: nitrite anion; NO3⁻: nitrate anion; NO
What is the role of nitrate ion for plants? - Quora
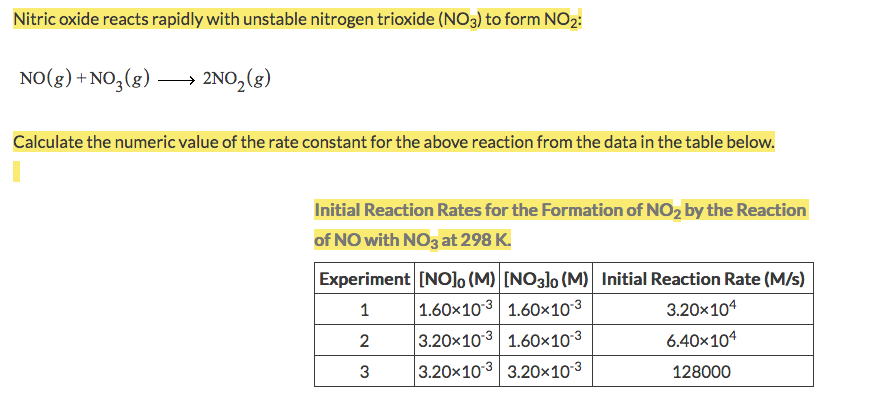
Solved Nitric oxide reacts rapidly with unstable nitrogen